This section describes how to deploy, verify, access, and uninstall RadonDB MySQL Operator and high-availability MySQL clusters.
Prerequisites
- Kubernetes cluster
- MySQL client tools
Procedure
Step 1 Add a Helm Repository.
Add a Helm Repository named radondb.
$ helm repo add radondb https://radondb.github.io/radondb-mysql-kubernetes/
Ensure that the chart named radondb/mysql-operator exists in the repository.
$ helm search repo
NAME CHART VERSION APP VERSION DESCRIPTION
radondb/mysql-operator 0.1.0 v2.1.x Open Source,High Availability Cluster,based on MySQL
Step 2 Deploy Operator.
Set the release name to demo and creates a Deployment named demo-mysql-operator.
$ helm install demo radondb/mysql-operator
This step also creates the CRD required by the cluster.
Step 3 Deploy a RadonDB MySQL Cluster.
Create an instance of the mysqlclusters.mysql.radondb.com CRD and thereby create a RadonDB MySQL cluster with default parameters as follows.
$ kubectl apply -f https://github.com/radondb/radondb-mysql-kubernetes/releases/latest/download/mysql_v1alpha1_mysqlcluster.yaml
To set cluster parameters, see Parameter Configuration.
Verification
Verifying RadonDB MySQL Operator
Check the demo Deployment and its monitoring service. The deployment is successful if the following information is displayed.
$ kubectl get deployment,svc
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
demo-mysql-operator 1/1 1 1 7h50m
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/mysql-operator-metrics ClusterIP 10.96.142.22 <none> 8443/TCP 8h
Verifying the RadonDB MySQL cluster
Run the following command to check the CRDs.
$ kubectl get crd | grep mysql.radondb.com
backups.mysql.radondb.com 2021-11-02T07:00:01Z
mysqlclusters.mysql.radondb.com 2021-11-02T07:00:01Z
mysqlusers.mysql.radondb.com 2021-11-02T07:00:01Z
Run the following command to check the cluster. If a statefulset of three replicas (RadonDB MySQL nodes) and services used to access the nodes are displayed, the installation is successful.
$ kubectl get statefulset,svc
NAME READY AGE
sample-mysql 3/3 7h33m
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/sample-follower ClusterIP 10.96.131.84 <none> 3306/TCP 7h37m
service/sample-leader ClusterIP 10.96.111.214 <none> 3306/TCP 7h37m
service/sample-mysql ClusterIP None <none> 3306/TCP 7h37m
Accessing RadonDB MySQL
You can use service_name or clusterIP to access RadonDB MySQL in the Kubernetes cluster.
RadonDB MySQL provides leader and follower services to access the leader node and follower nodes respectively. The leader service always points to the leader node supporting reading and writing data. The follower service always points to the read-only follower nodes.
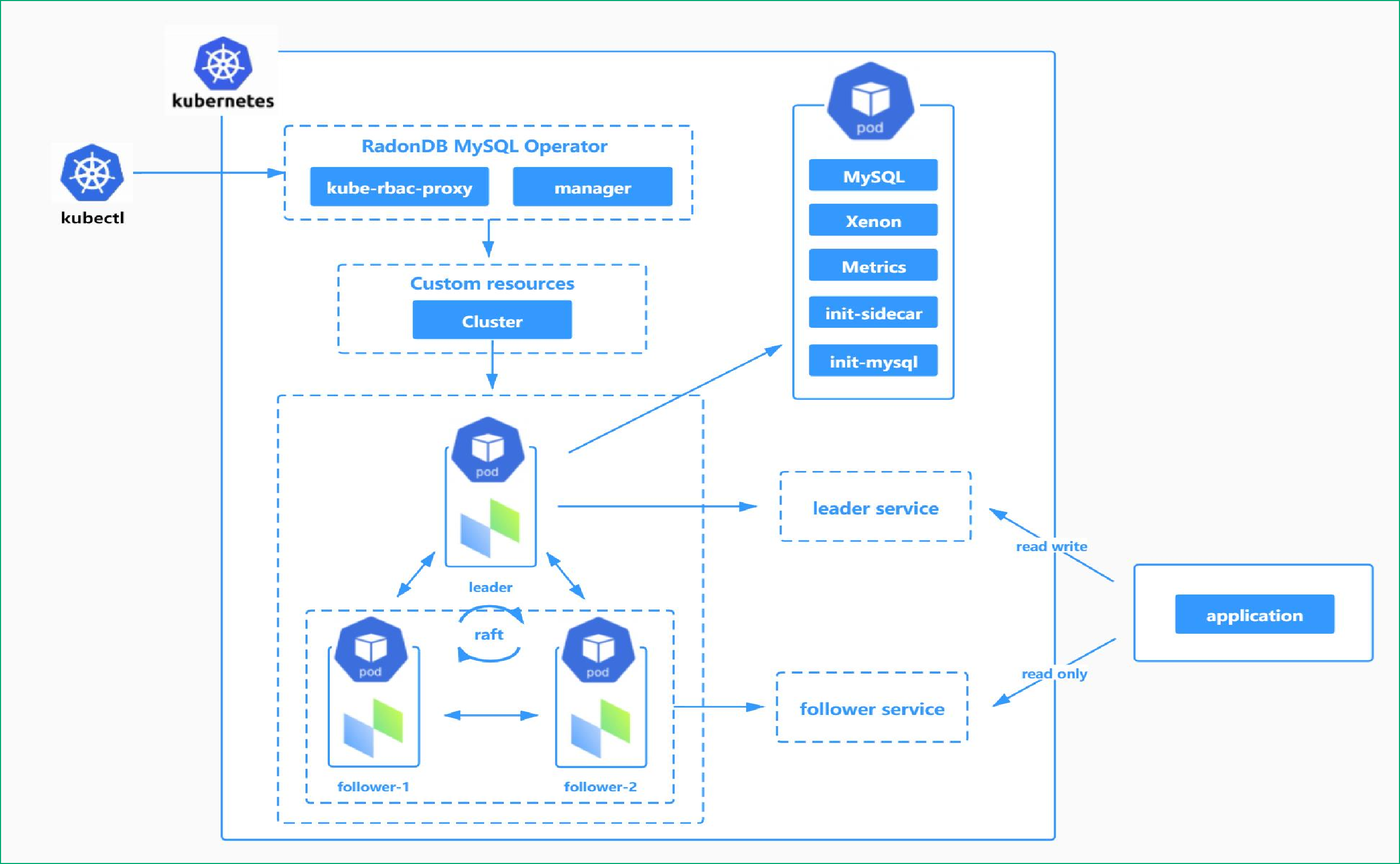
If the client and database are in the same Kubernetes cluster, access RadonDB MySQL as follows.
If the client is installed in a different Kubernetes cluster, see Access Applications in a Cluster to configure port forwarding and load balancing.
Using ClusterIP
The HA read/write IP address of RadonDB MySQL points to the clusterIP of the leader service, and the HA read-only IP address points to the clusterIP of the follower services.
$ mysql -h <clusterIP> -P <mysql_Port> -u <user_name> -p
For example, run the following command to access the leader service. The username is radondb_usr, and the clusterIP of the leader service is 10.10.128.136:
$ mysql -h 10.10.128.136 -P 3306 -u radondb_usr -p
Use a service_name
Pods in the Kubernetes cluster can access RadonDB MySQL by using a service name.
service namecannot be used to access RadonDB MySQL from the host machines of the Kubernetes cluster.
- Access the leader service (RadonDB MySQL leader node).
$ mysql -h <leader_service_name>.<namespace> -u <user_name> -p
For example, run the following command to access the leader service, where the username is radondb_usr, the release name is sample, and the namespace of RadonDB MySQL is default:
$ mysql -h sample-leader.default -u radondb_usr -p
- Access the follower service (RadonDB MySQL follower nodes).
$ mysql -h <follower_service_name>.<namespace> -u <user_name> -p
For example, run the following command to access the follower service. The username is radondb_usr, the release name is sample, and the namespace of RadonDB MySQL is default:
$ mysql -h sample-follower.default -u radondb_usr -p
Uninstallation
Uninstalling Operator
Uninstall RadonDB MySQL Operator with the release name demo in the current namespace.
$ helm delete demo
Uninstalling RadonDB MySQL
Uninstall the RadonDB MySQL cluster with the release name sample.
$ kubectl delete mysqlclusters.mysql.radondb.com sample
Uninstalling the Custom Resources
$ kubectl delete customresourcedefinitions.apiextensions.k8s.io mysqlclusters.mysql.radondb.com
$ kubectl delete customresourcedefinitions.apiextensions.k8s.io mysqlusers.mysql.radondb.com
$ kubectl delete customresourcedefinitions.apiextensions.k8s.io backups.mysql.radondb.com

